Task 2: Create a test environment
In this workflow, you’ll first get an access token. This enables you to call the subsequent requests in this workflow. Although you created an environment when you first signed on to your PingOne account, you’ll create an additional, new environment to use here, and for any subsequent testing you might want to do. You’ll then create a Population resource, and a new user for this population. Finally, you’ll assign the new user a password.
A new environment includes several PingOne resources automatically created for the environment (such as, a default sign-on policy, password policy, a default population, and defined notifications templates). This workflow uses the environment’s default sign-on policy and password policy to simplify the workflow.
The result
-
You’ll know how to get a PingOne access token for your Worker apps. For security purposes, access tokens have a 1 hour expiry, so you’ll use this request often.
-
You’ll now have a PingOne environment that you can use for testing, without impacting your initial environment.
-
You’ll know how to create populations, users, and assign users to populations, as well as how to assign user passwords. This is useful when you’re creating initial admin users. When creating or importing large numbers of users, you’ll use different techniques. Refer to Where to go from here for the documentation references.
If you choose to use Postman
If you don’t already have a Postman installation, you can install the free version. Refer to Download Postman.
-
Import or fork the Postman collection
Create your test environmentinto your Postman installation by clicking the Run in Postman button below. You’ll use this collection for this workflow: -
When you open the Postman collection, ensure that you select PingOne Postman Environment Template for use with the collection:

-
Refer to Postman and the PingOne APIs as needed for important information.
If you choose not to use Postman
If you’d rather not install Postman, this guide doesn’t limit or constrain you in that respect. Each Postman request is documented, and has a dropdown list to show the coding language to use for the request. (This is also true for our Platform Reference API documentation.)
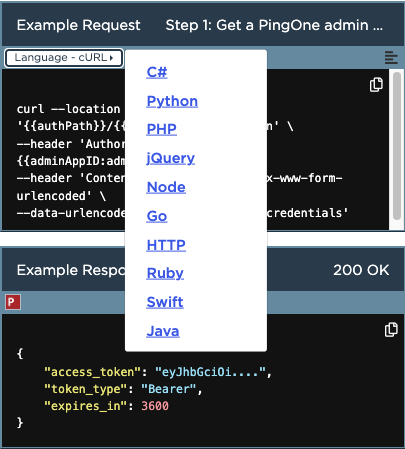
You can use cURL (the default) and call the request from your command line, or select one of the other coding languages in the dropdown list, copy the request into your IDE, and call it from there.