Tools
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents can extend their capabilities far beyond static training data by leveraging external tools to autonomously solve complex, real-world tasks. Tools are external functions, services, or APIs that an agent can invoke to perform specific actions, retrieve information, or augment reasoning.
Why tools matter
Tools allow AI agents to perform tasks that would be difficult using only their built-in knowledge. With tools, agents can:
- Access up-to-date information
-
Tools enable agents to query external knowledge sources in real time. For example, an agent might:
-
Query a company’s internal database to check a customer’s policy details
-
Access a public API to retrieve the latest stock prices
-
- Perform actions on behalf of users
-
Agents can interact with systems or services to execute tasks, such as:
-
Scheduling a meeting through a calendar API
-
Sending an email
-
Booking travel arrangements through an external service API
-
- Enhance reasoning and decision-making
-
Agents can leverage specialized tools to improve accuracy and efficiency, including:
-
Calculators or logic solvers for precise computation
-
Vector databases for semantic search or similarity queries
-
Analytics or simulation engines to evaluate complex scenarios
-
Integration with protocols
To ensure secure, auditable, and trustworthy tool usage, agents rely on protocols such as Model Context Protocol (MCP) and Agent-to-Agent (A2A).
- MCP
-
MCP provides a standardized framework for agents to discover and invoke tools securely. It enforces identity, authorization, and trust boundaries.
For example, an agent calling a sensitive HR API would require MCP-managed credentials and scopes to perform the action safely.
Learn more in What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
- A2A
-
Sometimes an agent delegates a subtask to another agent instead of calling a traditional API. The same security and trust principles apply: the calling agent must authenticate, obtain authorization, and interact according to organizational policies.
Learn more in What is Agent2Agent Protocol (A2A)?
How MCP and A2A work together
The emerging landscape of AI agents requires efficient collaboration and specialization. Complex tasks require not only individual agents but cohesive teams of agents, each excelling in a specific domain. MCP and A2A are the keys to enabling this sophisticated ecosystem.
Rather than competing standards, these two protocols are complementary. Each addresses a distinct, yet essential layer of the agentic architecture. An agent primarily uses A2A to communicate with other agents and MCP to interact with its specific tools and resources.
Think of MCP as vertical integration, that is, how a single agent interacts with the external world of tools, data, and APIs. It acts as the agent’s nervous system, standardizing the connection between a Large Language Model (LLM) and the resources required to complete a task.
In contrast, A2A addresses horizontal integration, which is how independent, autonomous agents communicate and collaborate as peers. A2A is the backbone of multi-agent architecture, governing the agent-to-agent communication that enables complex, multi-step workflows.
The following diagram illustrates how MCP and A2A work together to enable a seamless workflow from collaboration to execution:
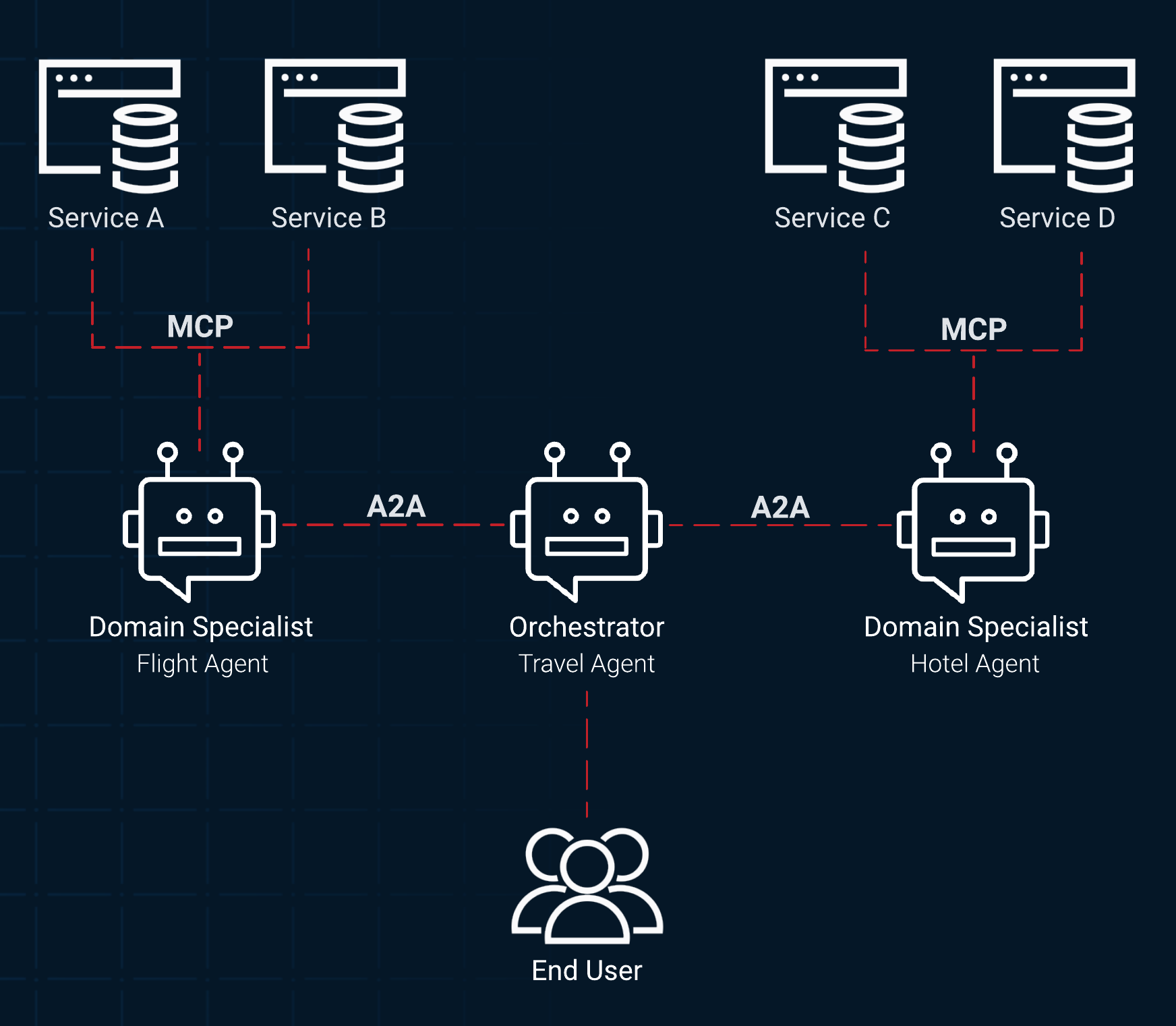
- Orchestration with A2A
-
A complex user request first goes to an orchestrating agent. This agent uses A2A to delegate sub-tasks to specialized peer agents. For example, a travel agent might use A2A to communicate with a flight agent and a hotel agent.
- Execution with MCP
-
Each specialized agent, having received its delegated task, uses MCP internally to perform the specific steps. The flight agent uses MCP to call the airline API tool to check prices, book a flight, and so on.
- Reporting with A2A
-
The specialized agents package the results of the tool executions as artifacts and return them to the orchestrating agent using the A2A protocol. The orchestrating agent synthesizes these results to provide a comprehensive, final answer back to the user.
By leveraging MCP and A2A capabilities, agents can access information, perform tasks, and collaborate with other agents while maintaining security, user consent, and auditability.