Authorize an AI Agent to Perform Tasks on Your Behalf
| This introduces our tutorial series. Check back often for new tutorials. |
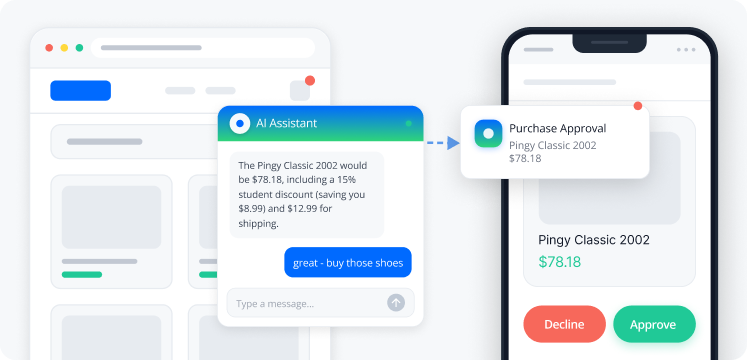
In this tutorial, a digital assistant agent helps customers research and purchase shoes from an online store. You’ll securely authorize your agent to perform tasks both autonomously and with explicit user approval. The agent will receive an access token it can then use to call tools and other agents. You’ll configure this using OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC) flows with PingOne Advanced Identity Cloud as the identity provider and authorization server.
This supports the following Identity for AI principles:
-
AI agents must always act on behalf of a user and never impersonate them.
-
AI agents should never directly prompt an end user for their credentials, but instead be granted tokens with least-privileged scopes after the user approves the transaction.
The agent will need to access tools such as "Get Latest Prices" which do not require user authorization but should still be secured. These are autonomous actions. This flow is detailed in Authorize autonomous actions with the Client Credentials flow.
When a customer wants the agent to assist with a user-specific task like shipping and purchasing, the agent accesses tools such as “Place Order” to act on behalf of the customer and use their information and payment details. The customer is sent a push notification to approve the transaction. These are on-behalf-of actions with a human-in-the-loop (HITL). This flow is detailed in Authorize on-behalf-of actions with CIBA.
Goals
-
Configure Advanced Identity Cloud identities for use by your existing AI agent
-
Configure the sign-on flows in Advanced Identity Cloud
-
Test the flows to receive an access token
-
Integrate the flows within your sample agent, allowing your agent to initiate authorization
What you’ll do
In this tutorial, you will:
-
Create demo identities in Advanced Identity Cloud to represent your end user and agent owner.
-
Create an application in Advanced Identity Cloud for your AI agent.
-
Authorize autonomous actions with the Client Credentials flow.
Agent architecture for Advanced Identity Cloud integration
Before integrating the OAuth 2.0 flows, consider that AI agents can be built using many different architectures. Some developers use frameworks like LangChain or LlamaIndex to manage prompts and tools, while others write custom agents in plain code for maximum control.
You can define tools locally within your agent’s code or manage them externally with an MCP (Model Context Protocol) server. You can also build some agents using hosted services like n8n or Zapier.
This tutorial focuses on a common and transparent pattern: a custom AI agent application written in TypeScript and run using Node that uses locally-defined tools.
This demonstrates the core security integration with Advanced Identity Cloud without the added abstraction of a specific framework or tool server. It shows how an agent can securely manage its own credentials to initiate flows and handle short-lived, access-controlled tokens that can be verified by the APIs it needs to access.
Core components of your sample agent
This tutorial assumes that you have a working prototype AI agent such to add authorization calls to. The following is a list of components your agent should have.
- Agent
-
The main agent logic that provides user requests to an LLM service together with a system prompt, conversation history, and information about the available tools. The LLM indicates when a tool should be invoked and with what arguments.
- Tool orchestrator
-
The tool orchestrator collates and presents tool definitions for the agent logic. In this example, it contains mappings between available tools and the authentication types and scopes that are required for the tool to interact with the APIs it relates to.
Example: Permission-aware tool configurationconst TOOL_AUTH_CONFIG = { 'getProducts': null, // Public access 'getAvailableDeals': { type: 'client_credentials', scope: 'prices' }, // Business API access 'getTailoredQuote': { type: 'ciba', scope: 'address' }, // User address data 'purchaseItem': { type: 'ciba', scope: 'payment' }, // Transaction consent };This mapping enables the tool orchestrator to automatically determine the level of authorization required before executing any tool, making the security integration transparent to the main agent logic.
- Advanced Identity Cloud authentication service
-
A dedicated module within the agent responsible for all communication with Advanced Identity Cloud. It handles both the Client Credentials and CIBA flows, abstracting the OAuth 2.0 complexity from other components.
Example: Clean abstraction for agent componentsclass PingOneAuthService { async getClientCredentialsToken(scope: string): Promise<string> async getCibaToken(scope: string, context?: string): Promise<string> } - Tools
-
The functions that perform actions, such as calling internal company APIs. Tools receive the appropriate access tokens from the tool orchestrator and use them to authenticate with the protected resources.
|
The agent application will have its own |
Before you begin
The tutorial assumes you have:
-
A basic understanding of PingOne Advanced Identity Cloud, OAuth 2.0, and OpenID Connect grant flows.
-
Access to an Advanced Identity Cloud tenant.
-
The PingID iOS or Android app configured to demonstrate the CIBA flow.
-
The Push Notification Service configured. You can find configuration instructions in tasks 1 to 3 in Login with MFA using push notifications in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
-
A working prototype AI agent to add authorization calls to. You can use a custom agent as shown in this tutorial, or one written with a framework like LangGraph.
If you do not have an AI agent that you can extend with the OAuth 2.0 flows, you can try out the flows in cURL or Postman.
Tasks
Create demo identities
-
In the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console, go to Identities, and then click Manage.
-
Click Alpha realm - users.
-
Create two identities: one for the end user and one for the app owner.
You’ll use the end user to register for push notifications with a device. You’ll use the app owner when setting up the OAuth 2.0 client. -
Click + New Alpha realm - User and create the end user identity using the form:
-
Username: end.user
-
First Name: End
-
Last Name: User
-
Email Address: end.user@example.com
-
-
Click Save.
-
Click + New Alpha realm - User and create the app owner identity using the form:
-
Username: app.owner
-
First Name: App
-
Last Name: Owner
-
Email Address: app.owner@example.com
-
-
Click Save.
Learn more in Create test users and roles in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
-
-
Create a Push Registration journey to allow the end user to register for push notifications, as the CIBA consent message will be delivered through the PingID mobile app.
The following is a minimum viable journey:
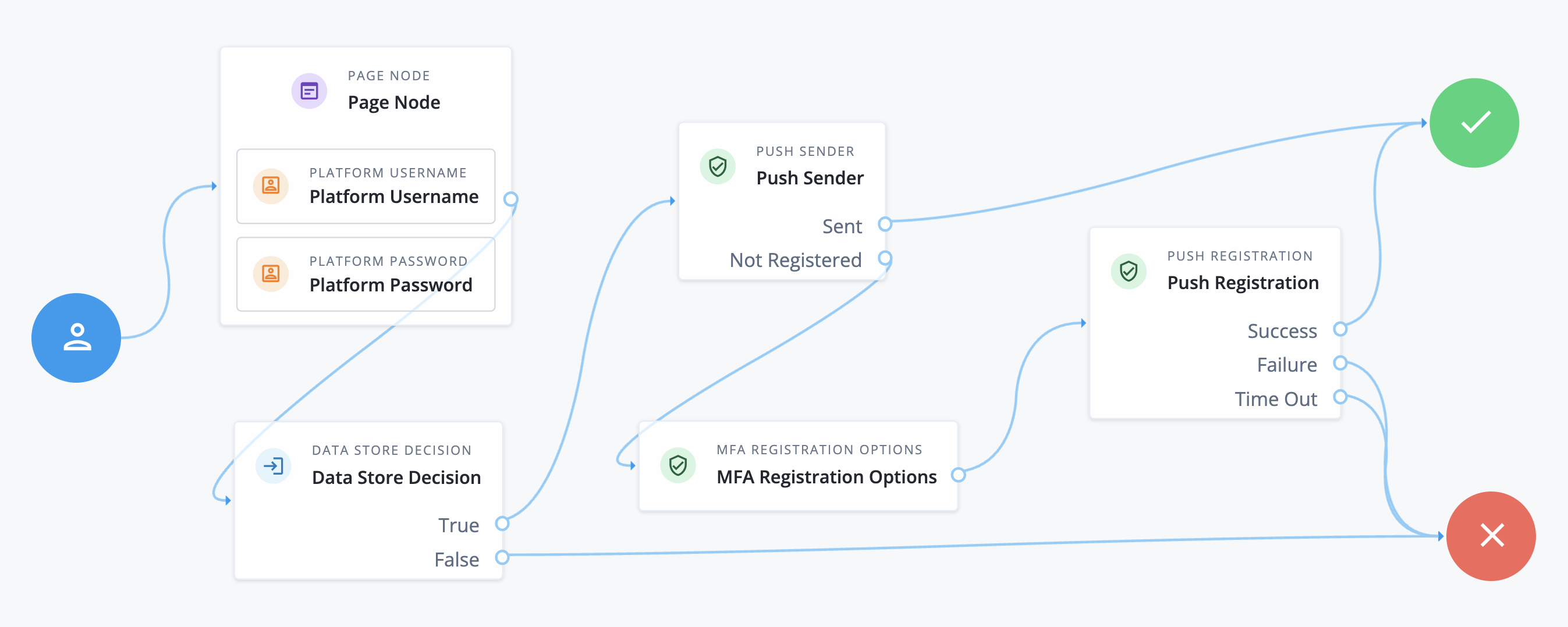
Learn more in Journeys and Push authentication journeys in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
-
Test the journey by running the journey’s Preview URL in a new incognito browser window as an end user.
Create an application
In this task, you’ll create an application that provisions an OAuth 2.0 client used by AI agent to request authorization.
-
In the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console, go to Applications and click + Custom Application.
-
When prompted for Sign-in Method, click OIDC - OpenID Connect and then click Next.
-
When prompted for Application Type, click Web and then click Next.
-
Enter a human-readable Name for your application, such as AI Agent. In the Owners list, select the app owner identity. Click Next.
-
Enter a Client ID, such as
ai-agent, and Client Secret and save them for later.The AI agent app will use the client secret to invoke OAuth 2.0 flows. -
Click Create Application.
Learn more about applications in Register a custom or SSO application in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
Next, you’ll configure the client for the required OAuth 2.0 flows.
Authorize autonomous actions with the Client Credentials flow
In this task, you’ll enable your agent to receive an access token on its own in cases where human authorization is not required. For example, accessing secured business APIs using tools like "Get available deals" that should be protected but don’t require specific user authorization.
The following diagram illustrates the authorization flow:
Learn more about this flow in Client credentials grant in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
-
Configure your application
-
In the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console, go to Applications and select the application you created in Create an application.
-
Click the Sign On tab and review the Grant types list. Add Client Credentials if it isn’t already listed.
This allows the client to request authorization by providing the client ID and secret you created earlier. -
Review the Scopes list and add a new scope called
prices.The token will use this scope when requesting pricing information. -
Click Save.
-
-
Verify the authorization flow by making the following REST call to get an access token that your agent could use with a tool endpoint (not provided):
$ curl --request POST \ --user '<client-id>:<client-secret>' \ --data "grant_type=client_credentials" \ --data "scope=prices" \ "https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/oauth2/realms/root/realms/alpha/access_token"
Result:
Advanced Identity Cloud returns an access token for your agent to use:
{ "access_token": "<access-token>", "scope": "write", "token_type": "Bearer", "expires_in": 3599 } -
Integrate with your agent
-
Implement the Advanced Identity Cloud token request by adding a function to your agent’s authentication service.
The following example shows how you can program an agent written in Node to fetch it’s own access token.
It uses the following environment variables for Advanced Identity Cloud integration.
Environment variable Value PINGONE_TOKEN_ENDPOINTThe token endpoint for your Advanced Identity Cloud environment, for example https://<your-tenant>.forgeblocks.com/am/oauth2/realms/alpha/access_token
PINGONE_CLIENT_IDThe client ID for the client created previously, for example
your-agent-client-idPINGONE_CLIENT_SECRETThe client secret for your client, for example
your-agent-client-secretShow example
/** * Requests an access token using Client Credentials flow * This is used for autonomous actions that don't require user permission */ async function getClientCredentialsToken(scope: string): Promise<string> { console.log(`Requesting client credentials token for scope: ${scope}`); // Create Basic auth credentials from environment variables const credentials = Buffer.from( `${process.env.PINGONE_CLIENT_ID}:${process.env.PINGONE_CLIENT_SECRET}` ).toString('base64'); // Make token request to P1AIC const response = await fetch(process.env.PINGONE_TOKEN_ENDPOINT, { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded', // Use Basic auth with base64 encoded client_id:client_secret 'Authorization': `Basic ${credentials}`, }, body: new URLSearchParams({ 'grant_type': 'client_credentials', scope, // Request specific scope (e.g., 'prices' for deals API) }), }); const data = await response.json(); console.log('Client credentials token obtained successfully'); return data.access_token; }
With this structure, the agent can now securely and efficiently call autonomous tools.
-
Authorize on-behalf-of actions with CIBA
In the previous task, you enabled an agent to request an access token for itself to use in a tool call which doesn’t require human authorization.
Next, you’ll implement a flow that allows your agent to call a tool on a human’s behalf and with their explicit permission through the form of a push notification.
Learn more about this flow in Backchannel request grant in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
-
Configure your application:
-
In the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console, go to OAuth2 Clients and select the application you created in Create an application.
-
Click the Sign-on tab.
-
Review the Grant types list and add Back Channel Request.
This will allow the client to request authorization from a human using the OIDC CIBA flow. -
Review the Scopes list and add a new scope called
address.The token will use this scope when requesting the end user’s information. -
Configure access to the relying party’s (RP’s) public keys so that Advanced Identity Cloud can verify JWT signatures:
-
In the General settings section, click Show advanced settings and then click Signing and Encryption.
-
In the Public key selector list, select JWKs.
-
In the JSON Web Key field, enter a JWK set similar to the following:
{ "keys": [ { "kty": "EC", "use": "sig", "crv": "P-256", "kid": "myCIBAKey", "x": "m0CkpWpZyGu-FLRLjCROVGC7Fwm5vGt8Lm3HhYU4ylg", "y": "U8NMtO-C2c3yhu2I_AzAELttmaitefPNPQaIJxvTCHk", "alg": "ES256" } ] }Learn more about Generating JWKs in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
-
Click Save.
-
-
-
Configure journeys:
-
Create a journey named Agent Push Sender similar to the following:
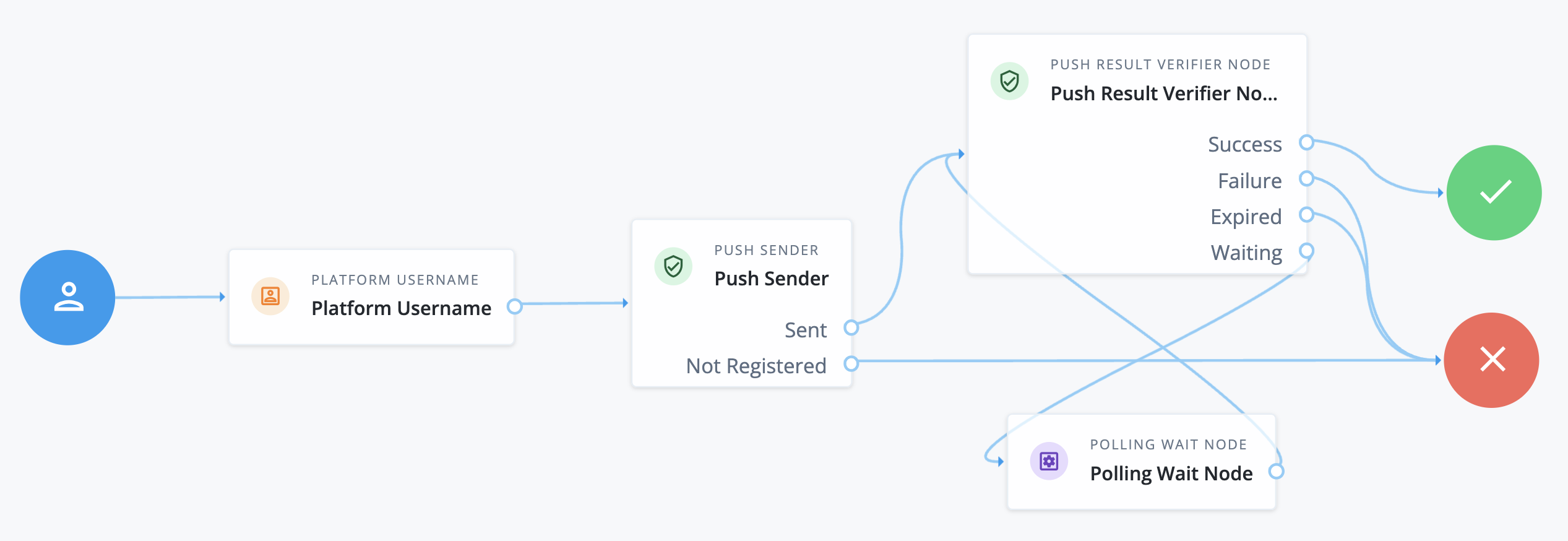
This minimum viable journey uses the following nodes:
Learn more in Push authentication journeys in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
To verify your journey, you can test it in your browser. After entering the end user’s credentials, you’ll be sent a push notification. -
In the Advanced Identity Cloud admin console, under Native Consoles > Access Management, go to Realms > Realm Name > Services > OAuth2 Provider > Advanced.
-
Make sure the Grant Types field includes Back Channel Request. Save any changes you make.
-
Associate the journey with incoming
acr_values:-
Go to the Advanced OpenID Connect tab of the OAuth 2.0 provider configuration.
-
In the OpenID Connect acr_values to Auth Chain Mapping box:
-
Set Key to the value that will be passed in through the
acr_valuesclaim of the incoming CIBA request, such aspush. -
Click Add.
-
Set Value to the name of your journey, such as Agent Push Sender.
-
-
Save your changes.
Learn more about the acr claim in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
-
-
-
Verify your integration:
You can now test the CIBA flow manually to ensure your Advanced Identity Cloud configuration is working before integrating with your agent. Execute the following REST calls to initiate the CIBA flow which should send a push notification to the end user. If approved, this will allow retrieval of an access token to call a tool on the user’s behalf.
-
Prepare a signed JWT with the required claims in the payload.
The example uses the following values:
Variable Value expA current timestamp plus 15 minutes. You can generate this in your terminal with
echo $(($(date -u +%s) + 899)).<rp-client-id>
Your client ID, such as
ai-agent.<end-user-id>
The username of the end user you created in Create demo identities, such as
end.user.{ "aud": "https://<tenant-env-fqdn>:443/am/oauth2/realms/root/realms/alpha", "binding_message": "Allow tutorial agent to access your address data?", "acr_values": "push", "exp": 1759988402, "iss": "<rp-client-id>", "login_hint": "<end-user-id>", "scope": "openid address" } -
Send a POST request to the
oauth2/bc-authorize/endpoint with the signed JWT in the payload. For example:curl \ --request POST \ --user '<rp-client-id>:<rp-client-secret>' \ --data 'request=<signed-jwt>' \ 'https://<tenant-env-fqdn>:443/am/oauth2/realms/root/realms/alpha/bc-authorize'
Learn more about generating JWTs in step 2 of Get an auth request ID in the Advanced Identity Cloud documentation.
Result:
-
You’ll receive a response similar to the following:
{ "auth_req_id": "abc123-def456-ghi789", "expires_in": 120, "interval": 5 }Make a note of the
auth_req_idas your agent will use it to poll for the result of the flow. -
Advanced Identity Cloud sends a push notification with the
binding_messageto the end user.
-
-
Poll for the access token by making a request to the Advanced Identity Cloud environment to determine the outcome of the flow. For example:
curl \ --request POST \ --user '<rp-client-id>:<rp-client-secret>' \ --data 'grant_type=urn:openid:params:grant-type:ciba' \ --data 'auth_req_id=<auth-req-id>' \ 'https://<tenant-env-fqdn>/am/oauth2/realms/root/realms/alpha/access_token'
Result:
After the end user has authorized the operation, Advanced Identity Cloud returns an ID token and an access token:
{ "access_token": "<access-token>", "refresh_token": "<refresh-token>", "scope": "openid profile", "id_token": "<id-token>", "token_type": "Bearer", "expires_in": 3599 }
-
-
Integrate with your agent:
-
Implement the CIBA flow within your agent. This involves creating the signed JWTs, initiating the CIBA request, and polling for user approval.
The following example shows how you can program an agent written in Node to fetch it’s own access token. It implements a new function,
getCibaToken, to manage the CIBA flow.It uses the following environment variables for Advanced Identity Cloud integration:
Variable Description PINGONE_CIBA_AUDIENCEYour Advanced Identity Cloud realm’s OAuth 2.0 provider identifier, for example https://<your-tenant>.forgeblocks.com:443/am/oauth2/alpha
PINGONE_CIBA_ACR_VALUESThe authentication context reference, linking to the push notification journey you set up earlier, for example
pushPINGONE_CIBA_ISSUERThe
client_idof the client issuing the requestPINGONE_CIBA_JWKThe JWK for signing CIBA requests stored as JSON string
PINGONE_CIBA_ENDPOINTThe backchannel authorization request endpoint for your Advanced Identity Cloud environment, for example https://<your-tenant>.forgeblocks.com/am/oauth2/realms/alpha/bc-authorize
This example requires libraries like jose for JWT signing. You must have a private key to use for signing. Show example
// Added around existing code from the Client Credentials section above import { SignJWT, importJWK } from 'jose'; // Type definition for CIBA initiate responses interface CibaInitiateResponse { auth_req_id: string; expires_in: number; interval: number; } /** * Creates a contextual binding message based on the scope and context. * This is displayed to users as part of the push notification */ function createBindingMessage(scope: string, context: string): string { switch (scope) { case 'payment': return context ? `Allow agent to place order for ${context}?` : 'Allow agent to place an order on your behalf?'; case 'address': return 'Allow agent to access your address information?'; default: throw new Error(`Unknown CIBA scope requested: ${scope}`); } } /** * Creates and signs a CIBA request JWT */ async function createCibaRequestJWT(scope: string, userId: string, context: string): Promise<string> { const bindingMessage = createBindingMessage(scope, context); const currentTime = Date.now(); const iat = Math.floor(currentTime / 1000); const exp = iat + 600; // Have the request be valid for 10 minutes const payload = { aud: process.env.PINGONE_CIBA_AUDIENCE, binding_message: bindingMessage, acr_values: process.env.PINGONE_CIBA_ACR_VALUES, // e.g., "push" exp, // expiration time for the authentication request iss: process.env.PINGONE_CIBA_ISSUER, login_hint: userId, scope: `openid ${scope}`, iat, // time at which the request was created nbf, // time before which the request is unacceptable }; // Import JWK and sign JWT const jwk = JSON.parse(process.env.PINGONE_CIBA_JWK); const privateKey = await importJWK(jwk, 'ES256'); const jwt = await new SignJWT(payload) .setProtectedHeader({ alg: 'ES256', typ: 'JWT', kid: jwk.kid, }) .sign(privateKey); return jwt; } /** * Initiates CIBA flow with P1AIC */ async function initiateCibaFlow(requestJWT: string): Promise<CibaInitiateResponse> { console.log('Initiating CIBA flow with P1AIC'); // Create Basic auth credentials const credentials = Buffer.from( `${process.env.PINGONE_CLIENT_ID}:${process.env.PINGONE_CLIENT_SECRET}` ).toString('base64'); const response = await fetch(process.env.PINGONE_CIBA_ENDPOINT, { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded', 'Authorization': `Basic ${credentials}`, }, body: new URLSearchParams({ 'request': requestJWT, }), }); const data = await response.json() as CibaInitiateResponse; return data; } /** * Polls for CIBA token after user approval */ async function pollForCibaToken(authReqId: string, interval: number): Promise<string> { console.log('Waiting for user approval...'); const maxAttempts = Math.ceil(600 / initialInterval); // 10 minutes max let attempts = 0; // Create Basic auth credentials const credentials = Buffer.from( `${process.env.PINGONE_CLIENT_ID}:${process.env.PINGONE_CLIENT_SECRET}` ).toString('base64'); while (attempts < maxAttempts) { // Wait before polling await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, interval * 1000)); attempts++; console.log(`Checking for approval (attempt ${attempts}/${maxAttempts})`); try { const response = await fetch(process.env.PINGONE_TOKEN_ENDPOINT, { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded', 'Authorization': `Basic ${credentials}`, }, body: new URLSearchParams({ 'grant_type': 'urn:openid:params:grant-type:ciba', 'auth_req_id': authReqId, }), }); const data = await response.json(); if (data.access_token) { // Success! The user approved return data.access_token; } if (data.error === 'authorization_pending') { // Continue polling continue; } else if (data.error === 'access_denied') { throw new Error('User denied the permission request'); } else if (data.error) { throw new Error(`CIBA error: ${data.error}`); } } throw new Error('CIBA flow timed out - user did not respond'); } } /** * Complete CIBA flow to get user permission token */ async function getCibaToken(scope: string, userId: string, context: string): Promise<string> { console.log(`Starting CIBA flow for scope: ${scope} and context ${context}`); // 1. Create signed JWT request const requestJWT = createCibaRequestJWT(scope, userId, context); // 2. Initiate CIBA flow const cibaResponse = await initiateCibaFlow(requestJWT); // 3. Poll for user approval const token = await pollForCibaToken(cibaResponse.auth_req_id, cibaResponse.interval); return token; } // Export the CIBA function along with client credentials export { getClientCredentialsToken, getCibaToken }; -
Update the tool orchestrator to obtain tokens using CIBA as needed.
Show example
import { getClientCredentialsToken, getCibaToken } from './P1AICAuthService'; import { getAvailableDeals } from './tools/getAvailableDeals'; import { placeOrder } from './tools/placeOrder'; // Tool configuration mapping tools to their auth requirements const TOOL_AUTH_CONFIG = { 'getAvailableDeals': { type: 'client_credentials', scope: 'prices' }, // Business API access 'placeOrder': { type: 'ciba', scope: 'payment' }, // Requires user permission //... other tool to authentication mappings }; /** * Permission-aware tool execution that handles different auth types * This is called by the main agent when the LLM decides to use a tool */ async function executeToolWithPermissions(toolName: string, args: Record<string, unknown>, userId: string) { // Look up what authorization this tool requires const authConfig = TOOL_AUTH_CONFIG[toolName]; let token if (authConfig?.type === 'client_credentials') { // Use Client Credentials to get access token from P1AIC for this scope token = await getClientCredentialsToken(authConfig.scope); } else if (authConfig?.type === 'ciba') { // Use context from args to create meaningful permission message const context = args.productName; token = await getCibaToken(authConfig.scope, userId, context); } // Execute the tool with the token return executeTool(toolName, args, userId, token); } /** * Central tool execution function that routes to specific implementations * This is where you add new tools as your agent capabilities grow */ private async executeTool(toolName: string, args: any, userId: string, token?: string): Promise<string> { switch (toolName) { case 'getAvailableDeals': return getAvailableDeals(token); case 'placeOrder': return placeOrder(args, userId, token); default: throw new Error(`Unknown tool: ${toolName}`); } } // Export for use by your main agent logic export { executeToolWithPermissions }; Step 3: Add the placeOrder tool The placeOrder tool is implemented similarly to the deals tool, but it will be calling a different and more sensitive API endpoint. // src/tools/placeOrder.ts export async function placeOrder(args: { productId: string; quantity: number }, userId: string, token: string): Promise<unknown> { try { const response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/purchase', { method: 'POST', headers: { 'Authorization': `Bearer ${accessToken}` }, body: JSON.stringify({ productId: args.productId, userId, quantity: args.quantity, }), }); const data = await response.json(); return data; } catch(error) { return `Failed to process purchase: ${error.message}`; } }
Your agent can now make on-behalf-of tool calls for the end user using the access token that was returned after the user authorized the operation.
-